
In this article, Emamou aims to provide a clear information about bioplastics, its types and applications.
GROUPS
Bioplastics include bio-based, biodegradable and compostable plastics. Bio-based means that the polymer is either entirely or partially obtained from biomass. Biodegradable means that the material can break down into natural substances such as CO2, water and biomass thanks to active microorganisms in the surrounding environment. Compostable plastics undergo biodegradation in home or industrial composting facilities where temperature (principally above 60oC) and surrounding conditions are structurally set.
Bioplastics therefore form three broad groups of polymers: 1) both bio-based and biodegradable, 2) only bio-based and 3) only biodegradable. Some main examples of bioplastics that are both bio-based and biodegradable are polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and bio-based polybutylene succinate (bio-PBS).
Polymer | Biobased | Biodegradable | Polymerization |
PBAT | No | Yes | Polycondensation reaction |
PBS | Yes | Yes | Melt polycondensation and chain extension |
PLA | Yes | Yes | Polycondensation or Ring-opening polymerisation |
PHA | Yes | Yes | Using microbes |
PET | No | No | Esterification and transesterification |
Bio-PET | Yes | No | Aqueous phase reforming and transesterification |
PCL | No | Yes | Ring opening polymerization |
PVA | No | Yes | Free radical vinyl polymerization |
Cellulose acetate | Yes | Yes | Cellulose with acetic acid |
Casein plastics | Yes | Yes | Precipitation using heat or acid |
APPLICATIONS
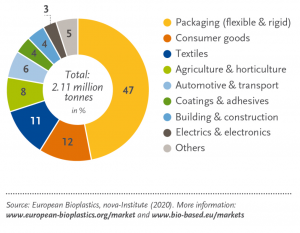
PROS: how to use bioplastics?
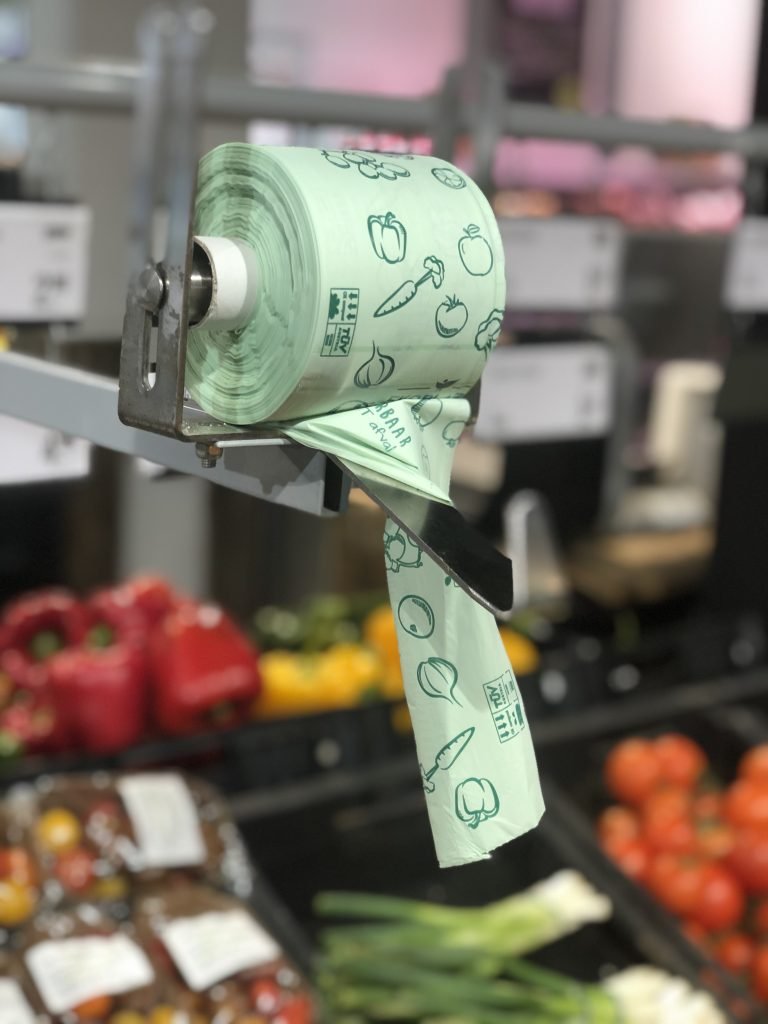
Recent years, bioplastics appear more and more on the consumer and industrial markets. You can find a variety of bioplastic products on online shops or in close-by supermarkets. Thanks to its bio-based resources, GHG emissions and environmental impacts of producing bioplastics are minor compared to the production of conventional plastics. Bioplastics do not have toxic chemicals, therefore they are good choices for food-related products such as vegetable bags, food containers, or food-contact gloves. They are also good options as trash bags collecting organic waste for municipal or industrial waste treatment and composting; or mulching films used in agriculture and horticulture to assure no contamination to the outside environment.
CONS: what aspects do we need to pay attention?
Bioplastics cause pollution concerns if they are not collected and treated properly. Bioplastic waste needs to be processed in an industrial composting facilities to be able to decompose completely and cause no harmful impacts. If it is leaked into the soil or waterway, it also takes years to decompose and the negative effects can override its advantages.
Labelling bioplastics also needs particular attention. There are still producers care for their profits more than for public health and the environment. They label their “fake” bioplastics (of low bio-based percentage and mixture with conventional plastics) and sell those products on the markets. They can also print a bioplastic name on the package without a proof of sustainability compliance. The consumers pay a higher costs and still our environment suffers further. Therefore, in the absence of a clear labelling or recognised certificate, consumers should avoid buying those products.
TIPs: for genuine bioplastics
2. Costs: There are no cheap bioplastics. If you see a pack of vegetable bags named “compostable bag” with a low price for conventional plastic bags, do not take them. They are likely “fake” bioplastics as explained above.
After reading this article, Emamou hopes that you are or keep remaining a responsible consumer, caring for your health and our planet!






